“Power comes to women who bring gay expectations to their heterosexual couplings.”
~ Jennifer Baumgardner
Mutually satisfying romance, love, and sexuality are teetering on the edge of failure in the modern heterosexual mating economy. Women are turning away from men and toward other women. Recognition and knowledge of female sexual fluidity may expand our understanding of human intimacy and improve the quality of heterosexual relationships, perhaps not a moment too soon. Let me start with a prescription and challenge to men and women in response to this trend. The rest of this post gives background and rationale for my “solutions,” focusing on nine formulations of context underlying female sexuality and fluidity.
What Can Be Done to Improve Heterosexual Partnerships
- Men (and women) need to learn much more about female sexual response, including sexual fluidity. Men need to accept and be curious about female sexual fluidity for what it can teach them.
- Men need to further develop the capacity for interpersonal intimacy and connected conversation. Creating that context is crucial for the future of heterosexual relationships.
- Men need to learn how to “interpret” the individual needs of women and create a sex-positive context specific for that woman.
- Women need to be patient with men as they learn and apply “gay expectations.”
- Women need to prefer men with high emotional intelligence over men with greater resources, status, and power. Establishing this preference is a very tall order for women because it runs counter to evolutionary pressures in mate selection. Female choice is always paramount. Women shape male behavior by their criteria for sexual access. The energetic and sexual charge between men and women must “diversify” (somehow) so that the alpha male does not always get the most desirable woman.
- Men need to reclaim the traits of heroic masculinity while monitoring and reducing particular forms of dominance. Servant leadership is the model. A man can be heroic without being “toxic.” Disengaging from the need for status and power is also a tall order. Male psychology has been shaped by hierarchy over thousands of years of mate selection in collusion with women.
- Women can readily encourage positive masculinity (heroic masculinity) by respecting and verbally acknowledging men for acts of service and by pushing back against the thinking that (all/most) men are “the problem.”
- Male sexuality should not be vilified as a malevolent force in nature but understood for its biological basis and evolutionary purpose. Political feminists who disparage or discourage male sexuality must acknowledge the sexual complexities of women concerning desire, power, and erotic objectification.
- American economic and social systems must allow average, working-class men to provide for their families and women to be supported in the workforce with a provision of care for their children.
Female Sexuality is Different from Male Sexuality
Women have their unique sexuality, like a fingerprint, and vary more than men in anatomy, sexual response, sexual mechanisms, and how their bodies respond to the sexual world. Women vary more widely from each other and change more substantially over their lifetime than do men.
Women’s sexual functioning includes sexual attractions, romantic affections, sexual practices/behaviors, and preference/orientation identities that are different from men’s sexual functioning due to biological and cultural adaptations.
Female sexuality is different from male sexuality in ways that affect all of us, all of the time.
What is Female Sexual Fluidity?
According to researcher Lisa Diamond, the fundamental and defining feature of female sexual orientation is fluidity (Sexual Fluidity — Understanding Women’s Love and Desire).
Diamond defines sexual fluidity as “situation-dependent flexibility in women’s sexual responsiveness that makes it possible for some women to experience desires for either men or women under certain circumstances, regardless of their overall sexual orientation.” Further clarifying is the definition of bisexuality by author Robyn Ochs (Getting Bi: Voices of Bisexuals Around the World): “A bisexual person has the potential to be sexually and/or romantically attracted to more than one sex, but not necessarily at the same time or to the same extent.”
Female Fluidity is Growing
Female sexual fluidity is on the rise. There is an increase in the percentage of women who identify as lesbian or bisexual in practice. Women are more likely to be “hetero-flexible” in their behavior than men, perhaps by a large margin. Researchers believe this has always been true, but it is a growing behavioral and cultural trend. Women are turning away from men for romance and connection; they prefer the company of women for a variety of socio-cultural reasons (e.g., response to memes of “toxic masculinity and the “me-too” movement).
A 2005 study by the Centers for Disease Control found that 11 percent of women aged 15-44 reported having some form of sexual experience with women; women were also three times more likely than men to have had both male and female partners in the last year. (1)
Liberal Generation Zs – An Increasingly Fluid Population
A recent Gallup poll found one in six (15.9%) Generation Z adults (ages 18-23) identified as LGBTQ. LBGTQ identification is lower in each older generation, including 2% or fewer respondents born before 1965. Young people who are politically liberal identified as LGBTQ at astronomical rates. Gallup found nearly thirty-one percent (30.7) percent of Gen Z liberal adults identified as LGBTQ. In 2021, female bisexual behavior is so common, the concept of “orientation” fits women less than men.
Bisexual women reveal preference instead of orientation.
Female Sexual Fluidity Reveals the Power of Context
Female sexuality is more context-specific than male sexuality. All external circumstances of everyday life influence the context surrounding a woman’s arousal, desire, orgasm, choice of partner, and orientation identity. Diamond observed, “the more we learn about women’s desires, the more obvious it becomes that they involve complex interplays between biological, environmental, psychological, and interpersonal factors.”
Formulations of Female Context
Related to fluidly and context, men and women are not the same sexual species.
Women’s sexual behavior and fluidity emerge out of several formulations of context.
1. Context of emotional connection
More than ever, women feel more emotionally connected to other women than to men. If this emotional trigger is strong enough, same-sex behavior as a preference can easily emerge. “Straight” women genuinely fall in love with other women; straight men do not often (or ever) fall in love with men in the same way.
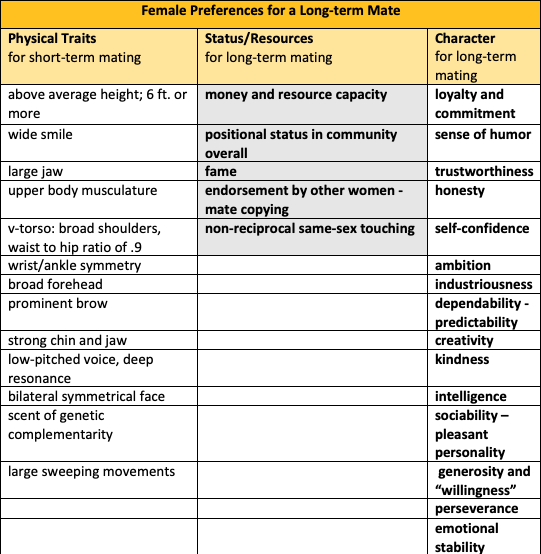
Women Have More Interest in the Character Traits of Connection
Men and women have different preferences and priorities for traits desired in a mate. While there is some agreement about preferring kindness, stability, humor, and care of children, women overall have much more interest in character traits that may bring interpersonal connection. Preference for interpersonal connection powerfully drives interest in same-sex behavior.
2. Context of being empowered and politically progressive
As extensively detailed by Jennifer Baumgardner (Look Both Ways – Bisexual Politics), female same-sex sexuality often emerged out of a political context. It provided a kind of virtue signaling – a badge of cultural wokeness. Female sexual fluidity was politically in alignment with the movement of women to equalize power dynamics and disengage from men and “structures of patriarchy.” Segments of the modern feminist movement have demonstrated strident but unexamined misandry. It has turned many women away from men as a political statement. Loving and being sexual with women becomes the correct political statement.
“Gay Expectations” – Contexts 1 and 2 Combined
“There are two reasons to be drawn to women when you are a woman,” explains Baumgardner. First, “being with a woman provides comfort. She is like the first person you bonded with, the nurturer; through her, you get understanding.” The second reason is political, she says, and forces this question: “Can I have a more satisfying, more equal relationship in which I like myself better with a woman?” Baumgardner answers this by saying, “I have yet to have a relationship with a man where I feel as strong and independent as I felt with the two serious female relationships I’ve had.”
“Gay expectations” are essentially the best traits in the character cluster of a heterosexual woman’s long-term mating strategy. Baumgardner says “power comes to women who bring gay expectations to their heterosexual couplings.” By “power” she means significant benefits of relationship satisfaction produced from asserting the need for a co-equal partnership with a man – a partnership where the woman also “brings” her criteria for emotional affinity. (To be clear, Baumgardner is not talking about a woman’s erotic power in a heterosexual partnership; Baumgardner may not even acknowledge the privilege of female erotic power.)
3. Context of being hip, renegade, and more sexually interesting
Bisexual or hetero-flexible women may be seen as more interesting, adventurous, and sexual than straight women. And, there is almost no downside for a woman to fall in love or want to have sex with a woman while continuing to attract men. Men are often more turned on by the thought of a woman who also loves a woman. Women who are sexual in a variety of ways are erotic for most men.
4. Context of belonging and community
“Membership” in the bisexual, “queer,” or lesbian community can often bring a powerful sense of belonging, especially for young adults. In an episode of The Bisexual, a young woman turns to the lead (bisexual) female character and says in a sense of comradeship, “well, you know, I am queer.” Our 30-something, experienced bisexual protagonist turns to her and says derisively, “well, everyone under 25 thinks they are queer.”
Belonging Is Intoxicating
Belonging is an intoxicating and essential human need. For marginalized or minority communities of any kind, belonging to a subculture is salvation. Sexually fluidity brings membership in a tribe that is counter to mainstream culture. It is potentially a provocative and charismatic club. Like a tattoo, it is an outward affectation that says, “I am adventurous; I am (paradoxically) unique and sexy.”
Dissension Within the Fluid Community
It is also true that there are subcultures and dissention within the fluid community, queer umbrella. Baumgardner details the struggles of bisexuals to be accepted within the lesbian community and the internal tensions about female sexuality within the feminist movement.
“Bi For Now”
We have witnessed popular terms such as “Lesbian until Graduation” (LUG) or “Bisexual until Graduation” (BUG) as sex researchers viewed college as a place where young women explore their sexuality and have their first and sometimes only lesbian relationship.
In 2003, a New Yorker magazine article, “Bi for Now,” suggested that women’s involvement in their college’s gay scene exposed them to a different culture, like a junior year abroad in “Gay World.” A large study (13,550 responses) by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that the prevalence of “gay until graduation” may be overestimated compared to non-college women. Yet, they also found the gender gap on homosexuality remained substantial: twice as many women as men reported same-sex behavior.
5. Context of men as undesirable and a liability
Men are perceived as less interesting and are less admired by women than ever before.
Being attracted to only men may even be seen as a liability, a disability, or just provincial. Women and the popular media often portray men as emotional and moral “children.” Sometimes bisexual women have to defend or hide their interest in men to self-identified lesbians.
6. Context of safety and a “sex-positive” situation
Women’s sexual functioning is influenced by their internal brain state — how they experience the present moment and how they generally think and feel about sex. Judgment, shame, stress, mood, trust, body image, and past trauma influence a woman’s sexual well-being. A woman’s brain must create a context that sees the world as a secure, pleasurable, and sexy place. A sex-positive context for a woman is a moment with low stress, high affection, high trust, and is explicitly safe.
What a woman wants and enjoys will change with her external circumstances and internal state. Women are often different from one another because a variety of contexts work to create female interest and readiness (female response variability).
7. Context of female competing intentions for erotic intimacy
Satisfaction in long-term relationships often requires balancing a polarity of human needs: safety, familiarity, attachment, and security on one pole, and adventure, risk, mystery, and novelty on the other. Bridging this polarity calls for a reconciliation between intimacy and caretaking (human bonding) and the sexual-erotic life, which often relies upon surprise and even distance.
Human beings want and need both sides of this polarity in order to experience optimal happiness. The need for familiarity and attachment may be a driver of same-sex behavior among women. But the need for distance or difference also seems to enter the equation of women’s sexual fluidity, especially for hetero-flexible or bisexual women. “One of the pleasures of the opposite sex is directly opposed to intimacy,” says Baumgardner. “It is the fact of our mysteries to them and theirs to us that fires some of the relationship.”
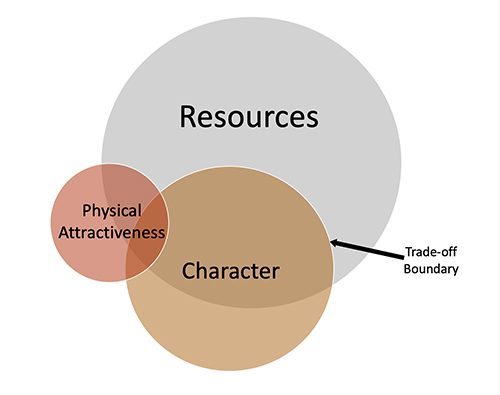
Female Sexual Fluidity Deals With Trade-offs Between Character and Power
Bisexual women want emotional bonding with women, the equality of sameness – politically, physically, and emotionally. Yet, as detailed by Baumgardner, bisexual women may also want the difference of a male body and the polarity of power experienced with a man – in a vaguely understood psychological soup of dominance and submission, subject and object. Baumgardner explains: “There is more to life than being a sex object. But the pleasure of being objectified – thought beautiful, sexy, special, and captivating – was drastically underplayed by feminists.”
“My sense of how hot and foxy a lover found me during sex had always been one of life’s greatest pleasures, and now I had trouble believing that this girl would or could objectify me.” ~ Jennifer Baumgardner
Author and bisexual sex researcher Lisa Featherstone was asked by Baumgardner what she learned from dating men that she could bring to her sexual relationship with a woman. “When I first started having sex with women, I remember thinking, I really like this, but I kind of want to be a little more attacked and objectified.” Featherstone continued: “It sounds weird, but you have more freedom to express the range of your sexuality to a man or another bi woman (than to a lesbian).”
Unconscious Double-binds
Below the “surface” of conscious awareness in hetero-flexible or bisexual women are complex unconscious factors and double-binds related to dominance, submission, desire to be desired, desire to be safe, and the internal struggle between preferring alpha traits of dominance and beta traits of kindness loyalty, and commitment. These are the same competing intentions of heterosexual women for long-term mating, amplified under the influence of modern feminism.
The “modern” woman must juggle her aspiration for personal power with her attraction to traditional forms of male power, embodied, not systemically, but in a particular man. She must also navigate trade-offs in mate selection between the apparent “polarities” of power and character. She wants both in different amounts at different times from the same person.
8. Context of supply and demand
One of the most potent “situations” in female heterosexuality is the workings of the overall mating economy – the impact of male spontaneous desire, initiation, and intrasexual competition. Sex for most women is an abundant resource; it is not in short supply. It is a need (within self-imposed selection preferences) that willing men can almost always meet. Therefore, there is no need to attend to it. If the refrigerator is full, there is no need to fantasize or strategize about getting food. If there is a man “pulling up” (like a bus) every 5 minutes, there is no need to worry about missing or choosing not to take the last bus.
In the recent opening episode (Half the Money) of Paramount’s Yellowstone, hard-charging Beth Dutton gives a woman direct advice on why she should stand up to her husband: “You have half the money and 100 percent of the pussy!” Enough said; Beth Dutton (and the writers of Yellowstone) understand female erotic power and its demand in the mating economy. This supply and demand dynamic is also salient for practicing bisexual women.
Supply and demand in the mating economy mostly encourages female sexual fluidity.
9. Context of physiological response, subjective desire, and sexual motivation.
As outlined in prior posts (see Appendix), female sexual fluidity is influenced by less testosterone and a weaker “sex drive” compared to men. Women operate primarily from “response-desire” and an “inhibition-braking” system, whereas men operate from “spontaneous-desire” and an “accelerator-excitation” system. Women also have very low “concordance” (agreement) between their subjective sexual desire and their physiological arousal compared to men. All of these factors influence the complexity of female sexual fluidity and undergird all other contextual factors.
Feminism Must Reconcile Complexities of Female Sexual Fluidity and Response
Positions of feminism that disparage or discourage male sexuality must recognize and reconcile the sexual complexities of women concerning desire, power, and objectification. Heterosexual feminist women sometimes disown the differences in male and female sexuality. Yet, they may desire “alpha male sexuality” and collude with it when it suits them. These complexities are also revealed in the multitudes of female sexual fluidity.
Male Sexuality Should Not Be Uniformly Criticized
We are in an era where masculinity itself is often considered toxic, not just specific inappropriate behaviors. The impact of the “me-too” movement is mainly a social good, but men are often lumped together as a singular class of predators. Male sexuality should not be vilified as a malevolent force in nature but understood for its biological imperatives. Men and male sexuality should not be criticized for “objectification” in many or most cases. Men are hard-wired and hormonally constructed to look and want. Bisexual and heteroflexible women (along with their heterosexual “sisters”) still “want to be wanted” and “erotically objectified” by men if the context is sex-positive.
The Drift Away from Men
Women are creating more distance from men, not less.
The “drift away” from men appears to be an exercise in preference, not orientation. Female sexual fluidity is emerging in a new context of romantic and sexual preference. The bisexual behavior of women may be uncovering an inherent female bisexual orientation, and it could also be an expression of disenchantment with men and masculinity in general. As the tee-shirt says, “the future is female.”
The Future of Male-Female Relationships
This “new” bisexuality and hetero-flexibility of women significantly influences the heterosexual mating marketplace – a marketplace that already favors the erotic power of women to choose and the struggles of men to be chosen. Studies have shown that female selectivity for mates is at an all-time high (except on college campuses with a surplus of women). Most men do not “make the grade” – they are not acceptable or attractive to women as mates. Preferences for same-sex relationships squeeze men even further out of the mating economy. Men often feel frustrated in their attempts to please women emotionally and sexually. The future of male-female relationships and heterosexuality depends upon understanding the fluidity of female sexuality emerging in young women (young millennials, Gen Z, and Gen Alpha). Like climate change, we may already be behind the curve in understanding and adapting to it.
Why does this matter?
Recognizing the sexual fluidity of women underscores the evolved behavioral sex differences between men and women. Acknowledging differences between male and female sexuality is a necessary starting point for improving male-female sexual partnerships. But the truth of evolved differences is often resisted by feminists. Pockets of academia continue to cling to a “blank-slate,” standard social science model that overemphasizes culture (“proximate” causes) and underemphasizes evolutionary biology (“ultimate” causes).
Cultural Forces Matter Going Forward
While accepting evolutionary biology and the tenets of mate selection science in the etiology of human sexuality, we must also acknowledge recent cultural forces that have increased female sexual fluidity. The growing disrespect of male heterosexuality and the drift away from men as sexual partners is probably not healthy or sustainable long-term. Solutions (“What can be done….?) must come through new knowledge and its application — perhaps a Sisyphean task considering ions of mate preference evolution and the rigidity of political-economic power structures, especially in the U.S.
Understanding Fluidity and Context Can Make Men Better Lovers
In conclusion, the understanding of female sexual fluidity and the formulations of female context can have an immediate positive impact on the quality of sexual relating for heterosexual couples, same-sex couples, and “queer” couple variations. (The effect on gay male couples is probably negligible.) It can significantly help men better understand female physiology, arousal, and the power of context.
Bottom line: understanding the power of context for female sexual fluidity can help men become better lovers for women.